BETA CAROTENE & CAROTENOIDS
Carotenoids are phytonutrients, the nutritional elements that occur naturally in
fruits and vegetables, giving them their distinctive yellow, orange or red
colors," Carotenoids also offer the plants protection from damage caused by
UV radiation and other environmental factors...just one of the many benefits
that recent research indicates may apply to humans.
Prepared By The Beesline® scientific Data Center (BSDC)2019
Between 500 and 600 specific carotenoids have been
identified. About 60 are found in foods and 20 in the
modern diet, only six are considered important for
human health 'namely, alpha carotene, beta carotene,
lutein, zeaxanthin, lycopene and cryptoxanthin.
Carotenoids are present in high levels in dark green,
yellow, orange and red fruits and vegetables --including
carrots, tomatoes, sweet potatoes, broccoli, spinach
and peppers. And although fruits and vegetables
contain a large number of carotenoids, the human body
only coverts carotenoids into vitamin A when it needs the
vitamin A. Therefore, Carotenoids are much safer than
vitamin A supplements.
CAROTENOIDS & UV PROTECTION
Dietary carotenoids from a healthy unsupplemented diet
accumulate in the skin and their level significantly
correlates with sun protection. Eating large quantities of
fish oil appears to provide a sun protective effect, in
some cases up to an SPF of 5, and may reduce the
UV-induced inflammatory response by a lowered
prostaglandin E2 levels (a mediator in the arachidonic
acid cascade for inflammation). In human fibroblasts,
lycopene, β-carotene, and lutein were all capable of
significantly reducing lipid peroxidation caused by UVB.
Natural Beta-Carotene will act as a protective as well as
a tanning agent for the skin, while it can protect against
sunburn to a certain extent.
ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY
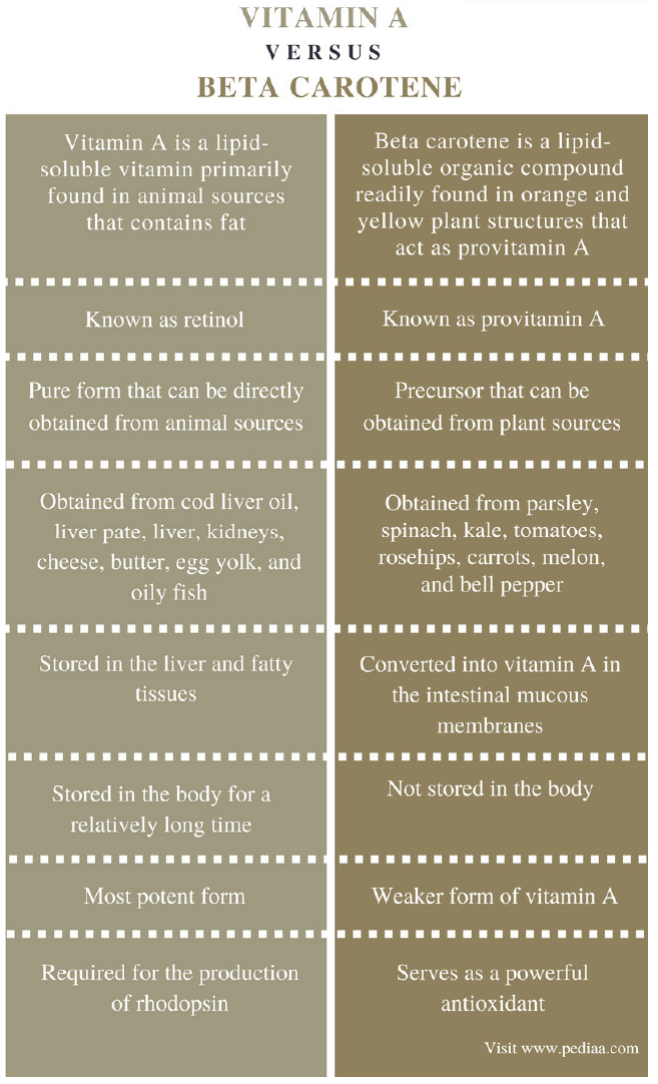
Beta-Carotene is a precursor to vitamin A, but has
important antioxidant functions, which cannot be
supplied by vitamin A. Natural beta-carotene has been
found to be up to 10 times as effective as synthetic
beta-carotene. Highly anti-oxidant, Beta-Carotene helps
reduce the risk of cancer, protects the body cells from
oxidation and prevents premature aging of skin as a
result of over exposure to the sun. It helps in healing of
scar tissue, because it has cellular renewal properties. It
is especially useful for acne sufferers. Beta-Carotene
helps also in removal of age spots, helps keep outer
layers of tissues and organs healthy.
Oral intake of Beta-Carotene offers cancer protection.
Research has shown a strong correlation between a
high intake of foods containing Beta-Carotene and lower
risks of cancer of the lungs and stomach, colon, prostate
and cervix. Carotenoids function as chain-breaking antioxidants, protecting cells and oth components from free radical
attacks. Oxidative damage resulting has been linked to the onset [of a variety] of degenerative diseases. Recent
scientific data suggest that optimal intake of carotenoids and other antioxidants can help delay the onset of cancer,
atherosclerosis, cataracts, macular degeneration and other major degenerative disorders.
One recent study focused on the effects of carotenoids-- specifically lutein and zeaxanthin--on age-related macular
degeneration--the leading cause of blindness among the elderly.
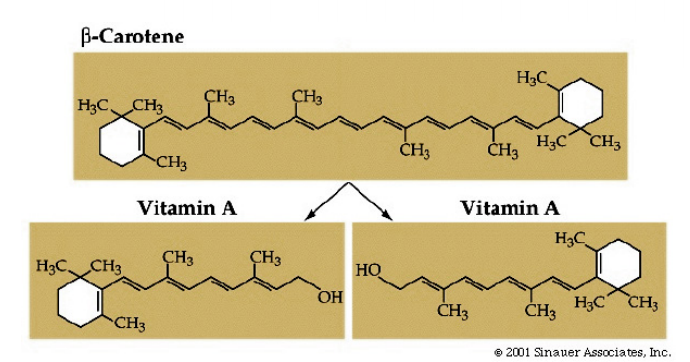
Commonly known as vitamin A, this term includes both retinol and its esters which can be transformed into retinal and
retinoic acid by metabolic processes. Plants contain no vitamin A, only carotenoids – or provitamin A - which can be
converted into retinol in the human or animal organism.
- Vitamin A plays an important part in building up the skin. This has become evident by demonstrating its stimulating
effects on the one hand and by analysing the consequences of vitamin A deficiency on the other.
- For example, vitamin A has been found to stimulate cell growth and act as a survival factor for fibroblasts in vitro. The
growth-stimulating effect of vitamin A is based on different mechanisms: Cell replication is stimulated, binding of
epidermal growth factor is increased and secretion of human growth hormone is induced.
- Vitamin A stimulates sebaceous gland activity, but does not cause excess secretion. Retinoic acid receptor inhibition
has been found to disrupt the epidermal barrier function.