SCIENTIFIC FACTS
UV RAYS & SUN DAMAGE ON THE SKIN
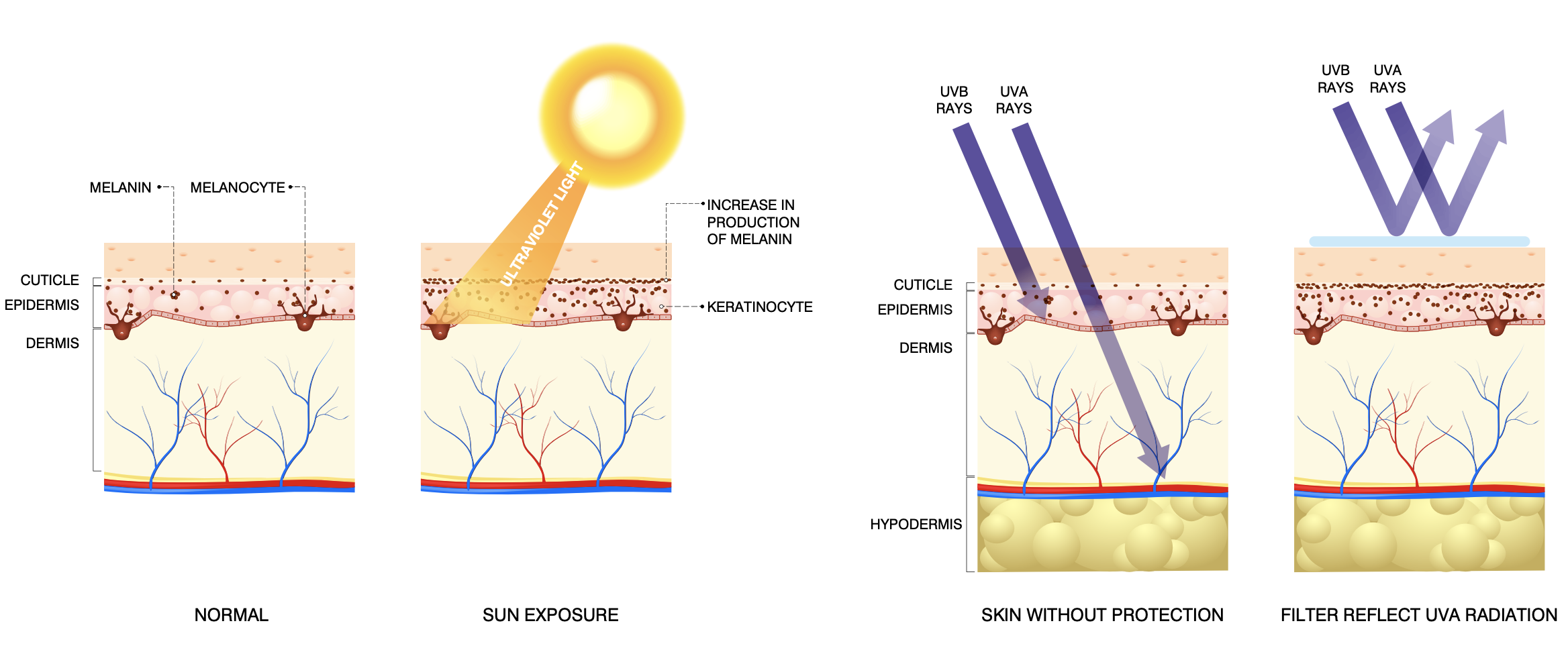
ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION
Electromagnetic radiation is broadly divided into infrared radiation (IR), visible light (VIS),
and UV radiation. Heat is part of IR radiation, which is not visible to the human eye. VIS
is the wavelength range of general illumination. UV radiation is divided into three distinct
bands in order of decreasing wavelength and increasing energy: UVA (400-320 nm), UVB
(320-290 nm), and UVC (290-200 nm). Different wavelengths and energy associated with UV
subdivision correspond to distinctly different effects on living tissue.
ULTRAVIOLET C RADIATION
UVC, although it possesses the highest energy and has the greatest potential for biological
damage, is effectively filtered by the ozone layer and is therefore not considered to be a
factor in solar exposure of human beings and is not of biological relevance.
ULTRAVIOLET B RADIATION
The amount of solar UVB and UVA reaching the earth›s surface is affected by latitude,
altitude, season, time of the day, cloudiness, and ozone layer. The highest irradiance is
at the equator and higher elevations. On the earth›s surface, the ratio of UVA to UVB is
1 :20. UV radiation is strongest between 10 am and 4 pm. During a summer day, the UV
spectrum that reaches the earth›s surface consists of %3.5 UVB and %96.5 UVA. UVB is
primarily associated with erythema and sunburn. It can cause immunosuppression and
photo-carcinogenesis.
ULTRAVIOLET A RADIATION
Because UVA is of longer wavelength compared with UVB, it is less affected by altitude
or atmospheric conditions. UVA, compared with UVB, can penetrate deeper through the
skin, and is not filtered by window glass. It has been estimated that approximately %50 of
exposure to UVA occurs in the shade.
In contrast to UVB, it is more efficient in inducing immediate and delayed pigment darkening
and delayed tanning than in producing erythema. UVA is known to have significant adverse
effects including immunosuppression, photo-aging, ocular damage, and skin cancer.
UVA rays are beneficial since they increase vitamin D3 production through the irradiation of
-7dihydrocholesterol. They intensify the darkening of preformed melanin pigment favoring
tanning. On the other hand, it has been demonstrated that these rays are responsible for
photosensitivity which result in several types of allergic reactions and actinic lesions.
DAMAGING EFFECTS OF ULTRAVIOLET
RADIATION
ACUTE RESPONSE OF HUMAN SKIN TO UVA & UVB IRRADIATION
- Erythema, UVB-induced erythema occurs approximately 4 hours after exposure, peaks
around 8 to 24 hours, and fades over a day or so; sometimes lasting for weeks, in fairskinned and older individuals. The effectiveness of UV to induce erythema declines
rapidly with longer wavelength. the same erythemal response, approximately 000 1
times more UVA dose is needed.
- Pigment darkening followed by delayed tanning, thickening of the epidermis and dermis, and synthesis of vitamin D. UVA is more efficient in inducing tanning,
whereas UVB is more efficient in inducing erythema.
- Sunburn appears immediately after the skin is exposed to UV radiation. Mild sunburn
causes only painful reddening of the skin, but more severe cases can produce tiny
fluid-filled bumps (vesicles) or larger blisters.
CHRONIC UVA & UVB EFFECTS
- Immunosuppression, and Photo-carcinogenesis.
- Actinic keratosis is a tiny bump that feels like sandpaper or a small, scaly patch of
sun-damaged skin that has a pink, red, yellow or brownish tint. Unlike suntan markings
or sunburns, an actinic keratosis does not usually go away unless it is frozen, chemically
treated or removed by a doctor. An actinic keratosis develops in areas of skin that have
undergone repeated or long-term exposure to the sun›s UV light, and it is a warning
sign of increased risk of skin cancer.
- Premature aging or photo-aging is when the skin develops wrinkles and fine lines
because of changes in the collagen of the dermis.
- Actinic purpura, UV radiation damages the structural collagen that supports the
walls of the skin›s tiny blood vessels. Particularly in older people.
ACTINIC PURPURA
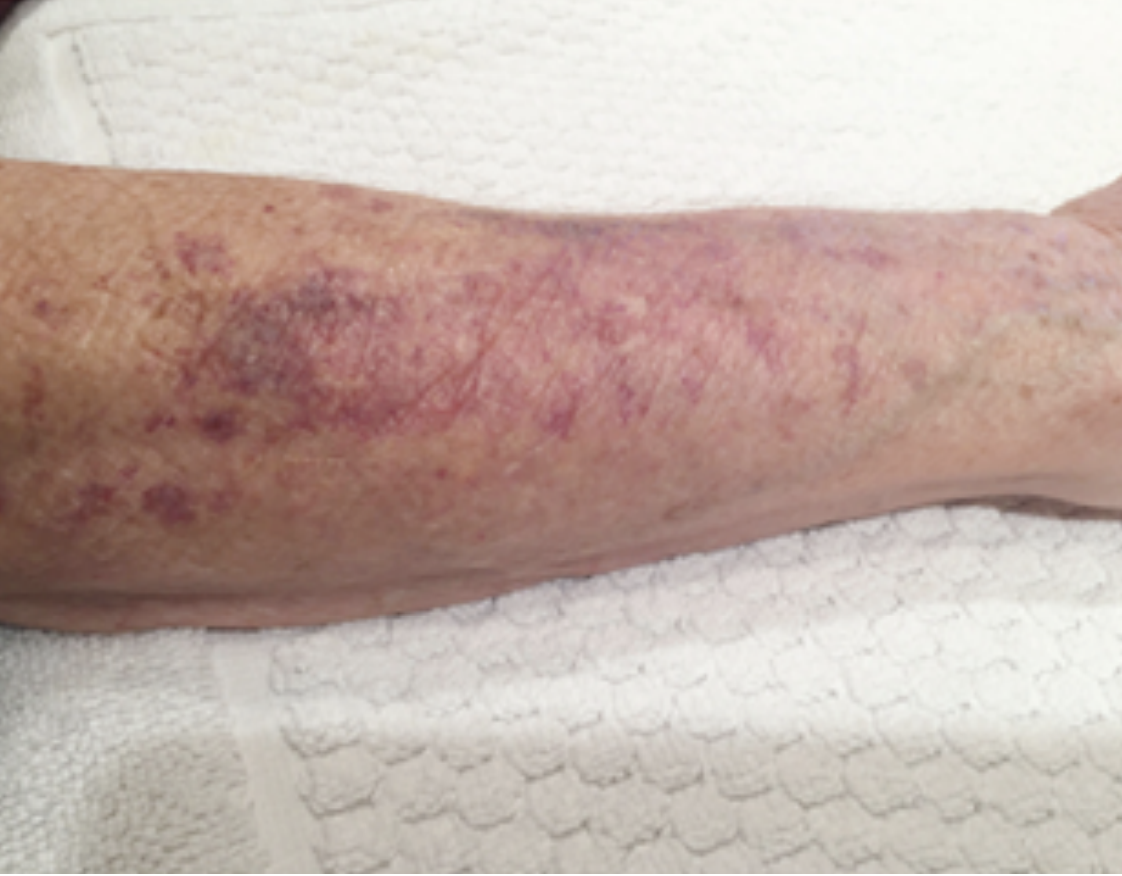
Before
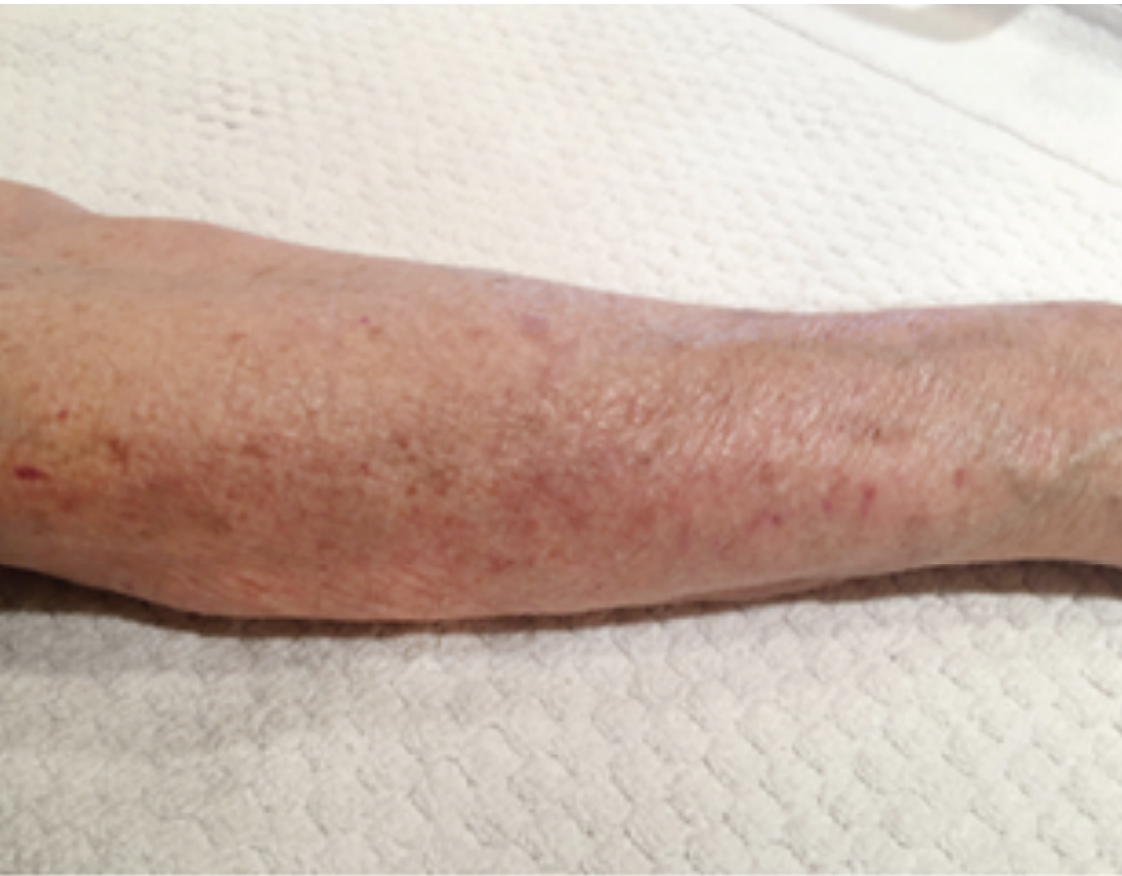
After
PREVENTION & CARE BY BEESLINE
We care about the skin health and have developed a wide Sun Protection Line in Beesline
with formulas made of the best:
- Sunscreen ingredients: called physical sunscreens, these are reflecting mineral
pigments, such as Zinc oxide & Titanium Dioxide. Used traditionally by indigenous
population, they stop %100 of the sun rays from entering & harming skin cells.
- Sun filtering ingredients: also called organic sunfilters, that absorb part of the
sunrays, but are invisible to the eye. These are neutralized by the sun rays, thus should
be constantly re-applied.
- Anti-oxidants: which protect skin against the aging effect of UVAs, they enhance skin
immunity and resistance.
Over a lifetime, repeated episodes of sunburn and unprotected sun exposure can increase
a person›s risk of malignant melanoma and other forms of skin cancer.
if you have fair skin and light eyes, you are at greater risk of sun-related skin damage and
skin cancers. This is because your skin contains less melanin.